Ixora auricularis Chun & F. C. How ex W. C. Ko: 베트남 미기록종
Ixora auricularis Chun & F. C. How ex W. C. Ko (Rubiaceae): A new record to Flora of Vietnam
Article information
Abstract
중국 운남의 고유종으로 알려진 꼭두서니과의Ixora auricularis Chun & F. C. How ex W. C. Ko가 베 트남에서 발견되었다. 이 종은 Ixora coccinea와 형태적으로 가장 비슷하지만, 잎의 기저는 이저이고, 측맥의 수가 많으며, 탁엽의 길이가 길고, 꽃받침 통의 길이가 짧으며, 화관의 끝이 도피침형, 화관내부의 부속체의 수가 더 많은 점에서 구분된다. 본 종에 대한 기재, 도해, 컬러사진과 함께 근연식물의 검색표를 제시하였다.
Trans Abstract
Ixora auricularis (Rubiaceae), previously recognized as endemic to Yunnan (China), was reported in Vietnam. This plant differs from the closely related species Ixora coccinea in its auriculate shape of the base leaf, greater number of secondary veins, shorter stipules, calyx having more appendices, shorter corolla tube, and the oblanceolata shape of the corolla tip. Detailed information about its description as well as illustrations, color photographs and a species key of related species of Ixora in Vietnam are provided.
Ixora is the third largest genus of the family Rubiaceae, comprising of about 500 species (Mouly et al., 2009) and commonly distributed in tropical Africa, America, Asia, Madagascar and Pacific islands (Tao and Taylor, 2011). Thirty four taxa of Ixora are confirmed in Indochina regions (Ganepain, 1923) and twenty three species and six varieties are distributed in Vietnam (Pham, 2003).
Recently, while checking herbarium specimen of Ixora in Herbarium of the Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources (HN) Hanoi, unidentified specimen which was collected from Van Ban (Lao Cai) in 2008 was found. At the same time, the same plant was also found during our recent field work from Xuan Lien Natural Reserve, Thuong Xuan district, Thanh Hoa province (19°59′32.78″N, 105°1′18.41″E) at an elevation of 510 m (Fig. 1, Fig. 2). The plant differs from a closely related species Ixora coccinea in auriculate shape of base leaf, more number of secondary veins, shorter stipules, calyx having more number of appendices, shorter corolla tube, oblanceolate shape of corolla tip (Table 1). On the basis of available literatures (Pham, 2003; Tao and Taylor, 2011) and carefully studying a type specimen of the plant, finally it was identified as Ixora auricularis Chun & F. C. How ex W. C. Ko for the first time from Vietnam. Previously its distribution has been known only in Yunnan of China. In this study, we reported Ixora auricularis as a newly added taxon to the Flora of Vietnam and its description, habitat, color photographs, illustrations and key of related taxa are provided.

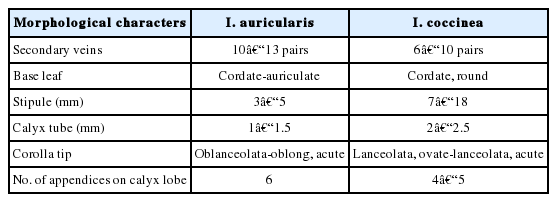
Ixora auricularis Chun & F. C. How ex W. C. Ko. A. Flowering twig. B. Leaf. C. Stipule. D. Flower triads. E. Flower. F, G. Calyx. H. Calyx lobe having six appendices. I. Stigma. J. Stamen. K. Young fruit (draw by Le Kim Chi, based on specimens VN 1965 (VN)).
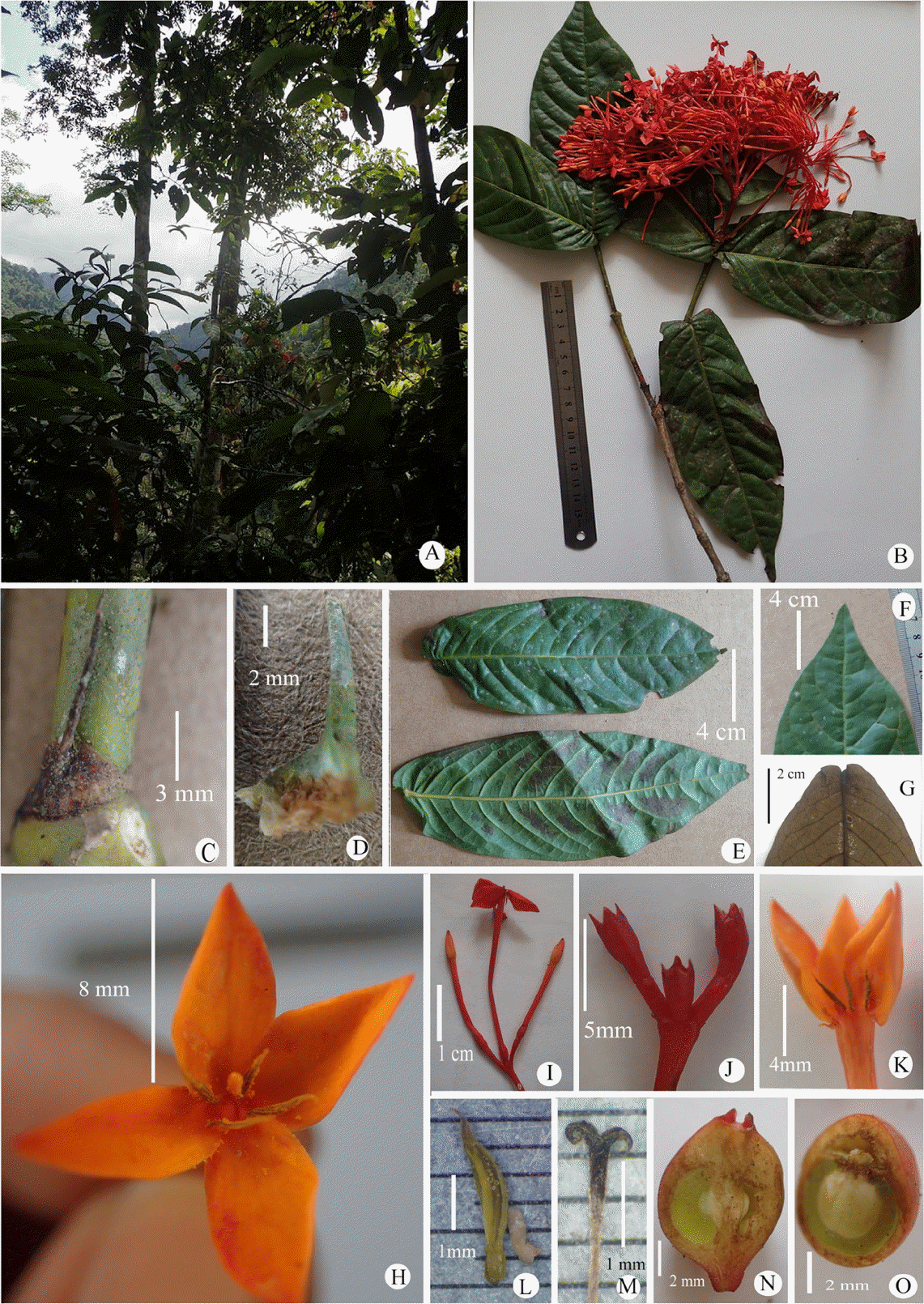
Ixora auricularis Chun & F. C. How ex W. C. Ko. A. Habitat. B. Flowering branch. C, D. Stipule. E. Leaf. F. Apical part of leaf. G. Base part of leaf. H. Flower. I. Inflorescence units. J. Calyx. K. Longitudinal section of flower. L. Stamen. M. Stigma. N. Longitudinal section of fruit. O. Cross section of fruit (A, Photo by Trịnh Ngọc Bon; B–O, photos by Thieu Thi Huyen Trang).
Taxonomic Treatment
Ixora auricularis Chun & F. C. How ex W. C. Ko, Guihaia 19: 99–100, 1999.—TYPE: China. Sino-Russian Exped. 2347 (SCBI).
Shrubs or small trees up to 6–10 m high. Young branches glabrous, green. Leaves opposite, sessile; blade oblanceolate, oblong elliptic, or obovate-elliptic, 10–23 × 5–9 cm, glabrous on both surfaces, base cordate-auriculate, apex shortly acuminate, drying thinly papery, brown adaxially, pale abaxially; secondary veins 10–13 pairs; stipules broadly triangular, 7–18 mm, awn of stipules 5–7 mm, seta inside. Inflorescences terminal, corymbose, 6–15 cm wide; axis pubescence; peduncle 3–5 cm, articulate near base, at articulation with reduced leaves ca. 3 cm; bracteoles linearlanceolate, ca. 1 mm; pedicels 2–3 mm. Flowers sessile or pedicellate. Calyx with hypanthium obconic, tube 1–1.5 mm; limb deeply lobed; lobes 4, ligulate, 0.5 mm long, having 6 appendices. Corolla purplish red; tube 2–3.5 cm, glabrous at throat; lobes oblanceolate-oblong, 7 × 3 mm, apex acute, sparse hair at base. Stamens 4, short filaments 1 mm; anthers 3 mm, acute at tip, bilobate at base. Ovary 2 loges, one ovule per loge; stigma bipartite. Drupe globose, 6–8 mm in diam..
Habitat: The species growing in evergreen forested.
Flowering: May–Jun.
Distribution: Vietnam (Lao Cai, Thanh Hoa), China (Yunnan).
Specimens examined: VIETNAM. Lao Cai province: Van Ban, 2008, Nguyen Quoc Binh et al. VN 1965 (VN); Thanh Hoa province: Thuong Xuan, 2016, Nguyen Dinh Hai et al. Trang-005 (VN).
A key to Ixora auricularis and its related taxa in Vietnam
1. Petiole 0–2 mm.
2. Stipule 3–5 mm, calyx tube 1–1.5 mm ······················· ································································· I. auricularis
2. Stipule 7–18 mm, calyx tube 2–2.5 mm.
3. Leaves longer than 5 to 20 cm; wider than 3 to 5 cm.
4. Secondary veins of leaves 6–10 pairs ·········································································· I. coccinea
4. Secondary veins of leaves 12–16 pairs ················································· I. coccinea var. caudata
3. Leaves shorter than 2 to 4 cm; narrower than 1 to 1.5 cm ·························· I. coccinea var. compacta
1. Petiole longer than 5 mm.
5. Calyx lobe longer than ovary ············· I. eugenioides
5. Calyx lobe shorter than ovary or same length.
6. Pubescence at corolla throat ··················· I. laotica
6. Glabrous at corolla throat.
7. Petiole 1–2 cm, stem slightly stout, style hairy in the middle ·········································· I. casei
7. Petiole 0.5–0.8 cm, stems slender, style glabrous ······························································ I. fulgens
Acknowledgements
We thank to Korea Research Institute of Bioscience & Biotechnology (KRIBB), Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST) Hanoi, all members of department of botany at Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources (IEBR), Vietnam and Korea and The National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NRF-2016K1A1A8A 01939075) for supporting this study. We also deeply thank Mr. Trinh Ngoc Bon for supporting fieldtrip and Mrs. Kim Chi for illustration.