Artemisia kargilensis (Asteraceae), a new species from Ladakh (Trans-Himalaya), India
Article information
Abstract
A new species, Artemisia kargilensis, is described here from Ladakh (Trans-Himalaya), India. The new species can be distinguished from its allied congeners Artemisia salsoloides Willd. and A. saposhnikovii Krasch. ex Poljakov in having leaves sessile, leaf rachis winged, leaf segments linear to linear-lanceolate, capitula globose and upright, pedicel 2–5 mm long, bracteole linear, margins flat, apices acuminate, involucre 3-seriate, outermost phyllary ovate, innermost phyllary broadly obovate, number of marginal female florets 8–18, number of disc florets 16–28, and achenes obovoid.
INTRODUCTION
Artemisia L. is the largest genus of the tribe Anthemideae (Asteraceae). It comprises about 300–500 species, distributed mainly in the Northern Hemisphere (Ling, 1991; Shulz, 2006; Ling et al., 2011; Pellicer et al., 2014). The genus is generally divided into five subgenera: Artemisia L., Absinthium DC., Dracunculus Besser, Seriphidium (Besser ex Lessing) Fourr., and Tridentatae (Rydb.) McArthur (Shultz, 2006).
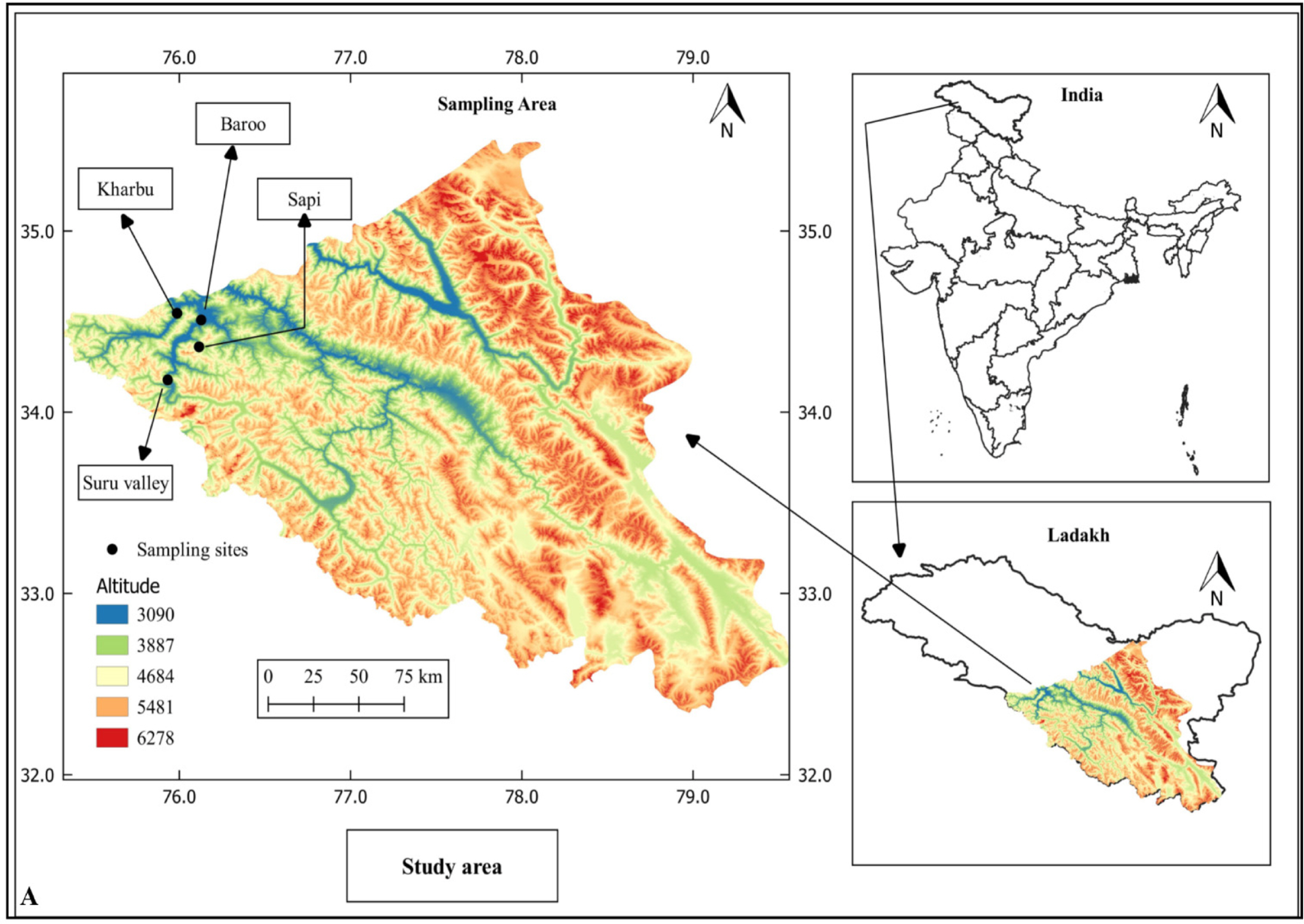
As of now, a total of 40 species of Artemisia have been reported from India (Singh et al., 2019). In India, Artemisia is mostly distributed in the Himalayas (Kaul and Bakshi, 1984; Ali et al., 2023). During our recent field surveys on account of systematic studies on the genus Artemisia, we collected specimens of distinctive Artemisia taxon from the Trans-Himalayan region of Ladakh, India (Fig. 1). Based on staminate disc floret, and abortive achene, the distinctive Artemisia taxon were referred to A. subg. Dracunculus and found to have gross morphological similarity with A. salsoloides Willd., and A. saposhnikovii Krasch. ex Poljakov. However, further critical investigation of the collected specimens, scrutiny of relevant literature and herbarium specimens revealed that they represent a hitherto undescribed species within this subgenus by having leaf rachis winged, marginal female florets 8–18, disc florets 16–28, capitula globose, pedicel 2–5 mm long, bracteole linear, 2–6 mm long, margins flat, apices acuminate, involucre 3-seriate, outermost phyllary ovate, innermost phyllary broadly obovate, and achenes obovoid.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The plant specimens were collected from various sites in Kargil district of Ladakh: Suru valley, Kharbu, Baroo, and Sapi (Fig. 1). Standard taxonomic procedures were followed for collection, drying, and further processing of the herbarium specimens (Bridson and Forman, 1998). The collected plant specimens were compared with the protologue of A. salsoloides (Willdenow, 1803) and A. saposhnikovii (Poljakov, 1961), as well as with the other relevant taxonomic literature (Hooker, 1882; Hajra et al., 1995; Ghafoor 2002; Ling et al., 2011). We also examined the herbarium specimens of A. salsoloides deposited in KASH, DD, BSD, K, GDC, LINN, and A. saposhnikovii deposited in NHM-P, BR, and E (Herbaria acronyms as per Thiers, 2023). For studying and measuring macro- and micro-morphological characters of A. kargilensis and A. salsoloides, we used ten individuals of both the taxa. The capitula were studied by keeping them in FAA solution for 24 h and then the samples were rinsed with water, different parts of inflorescence were placed on slide and Hoyer’s solution were used for microscopic studies (Anderson, 1954). Finally, the samples were examined and photographed under stereo microscope (Leica S9D, Mannheim, Germany) integrated with image processing software (LASX). The map showing the distribution of A. kargilensis was prepared using QGIS software, version 3.20 (QGIS, 2022).
TAXONOMIC TREATMENT
Artemisia kargilensis L. Ali, A. A. Khuroo & A. H. Ganie, sp. nov.–– INDIA. Ladakh, Kargil district, Suru valley, 34°10′41.52″N, 75°55′56.07″E, elev. 3,200 m a.s.l, 23 Jul 2020, Liyaqat Ali, Anzar A. Khuroo & Aijaz H. Ganie 38592 (holotype: KASH!, isotype KASH!) (Figs. 2, 3).

Photographs of Artemisia kargilensis. A. Habitat. B. Habit. C. Inflorescence. D. Leaf. E. Bracteole. F. Phyllaries. G. Capitula. H. Receptacle. I. Corolla (marginal female floret). J. Corolla (disc floret). K. Pistil (marginal female florets). L. Pistil (disc floret). M. Achene.
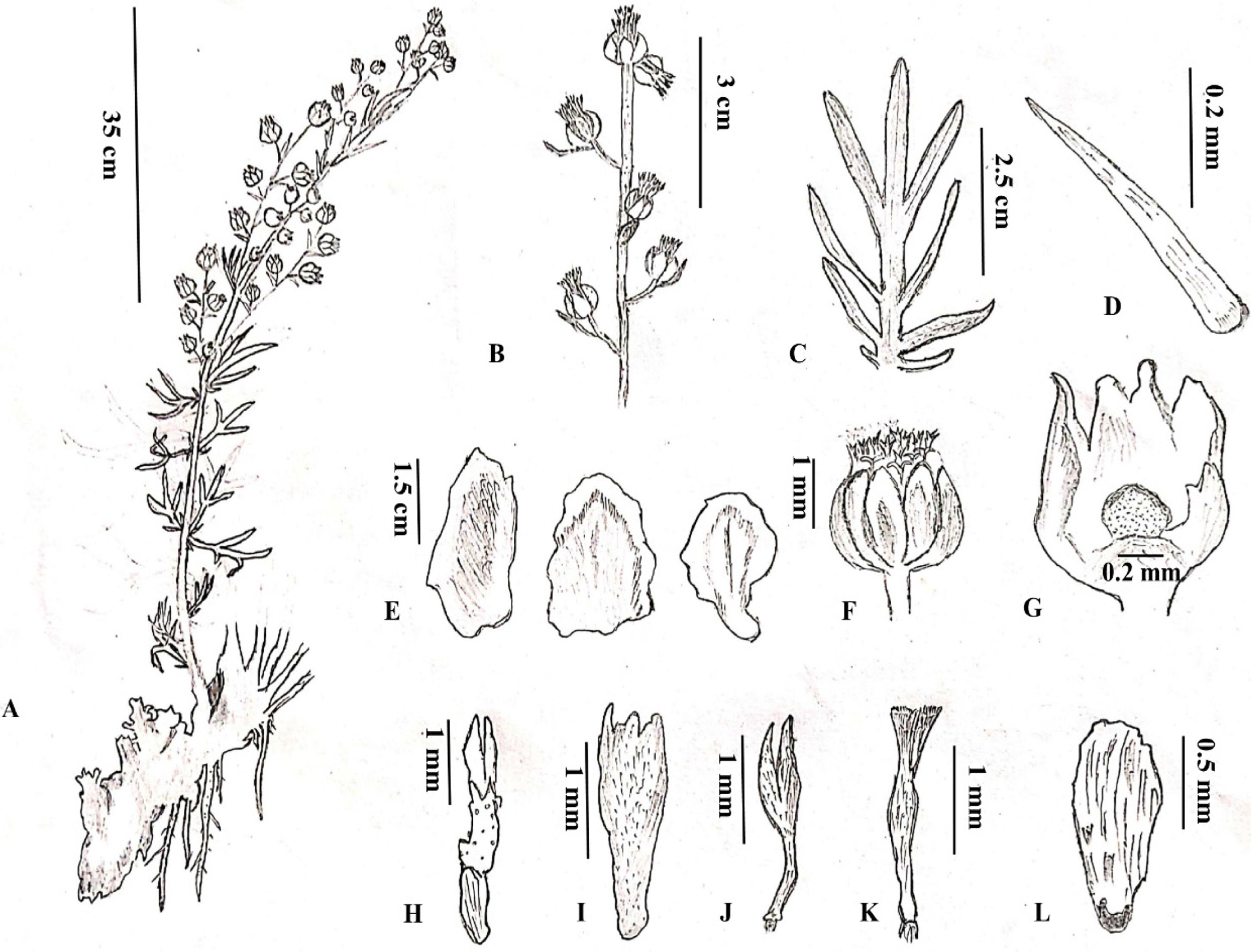
Illustrations of Artemisia kargilensis. A. Habit. B. Inflorescence. C. Leaf. D. Bracteole. E. Phyllaries. F. Capitula. G. Receptacle. H. Corolla (marginal female floret). I. Corolla (disc floret). J. Pistil (marginal female florets). K. Pistil (disc floret). L. Achene.
Artemisia kargilensis is most similar in morphological with A. salsoloides but differs in having habit 40–70 cm tall, leaf sessile (vs. subsessile), leaf rachis winged (vs. wingless), linear to linear-lanceolate (vs. linear to linear-oblong), marginal female florets 8–18, disc florets 16–28 (vs. marginal female florets 15–20, disc florets 10–14), capitula globose, upright (vs. oblong, upright to nodding), pedicel 2–5 mm long (vs. sessile to shortly pedicellate), bracteole linear, 2–6 mm long, margins flat (vs. oblong, 2–4 mm long, margins recurved), involucre 3-seriate (vs. 4-seriate), outermost phyllary ovate (vs. linear-oblong), innermost phyllary broadly obovoid (vs. ovoid to narrowly obovoid), and achenes obovoid (vs. oblong). In addition, the new species also varies in habitat elevational range of 2,300–3,200 m a.s.l. (vs. 2800– 3900 m a.s.l) (Fig. 4, Table 1).
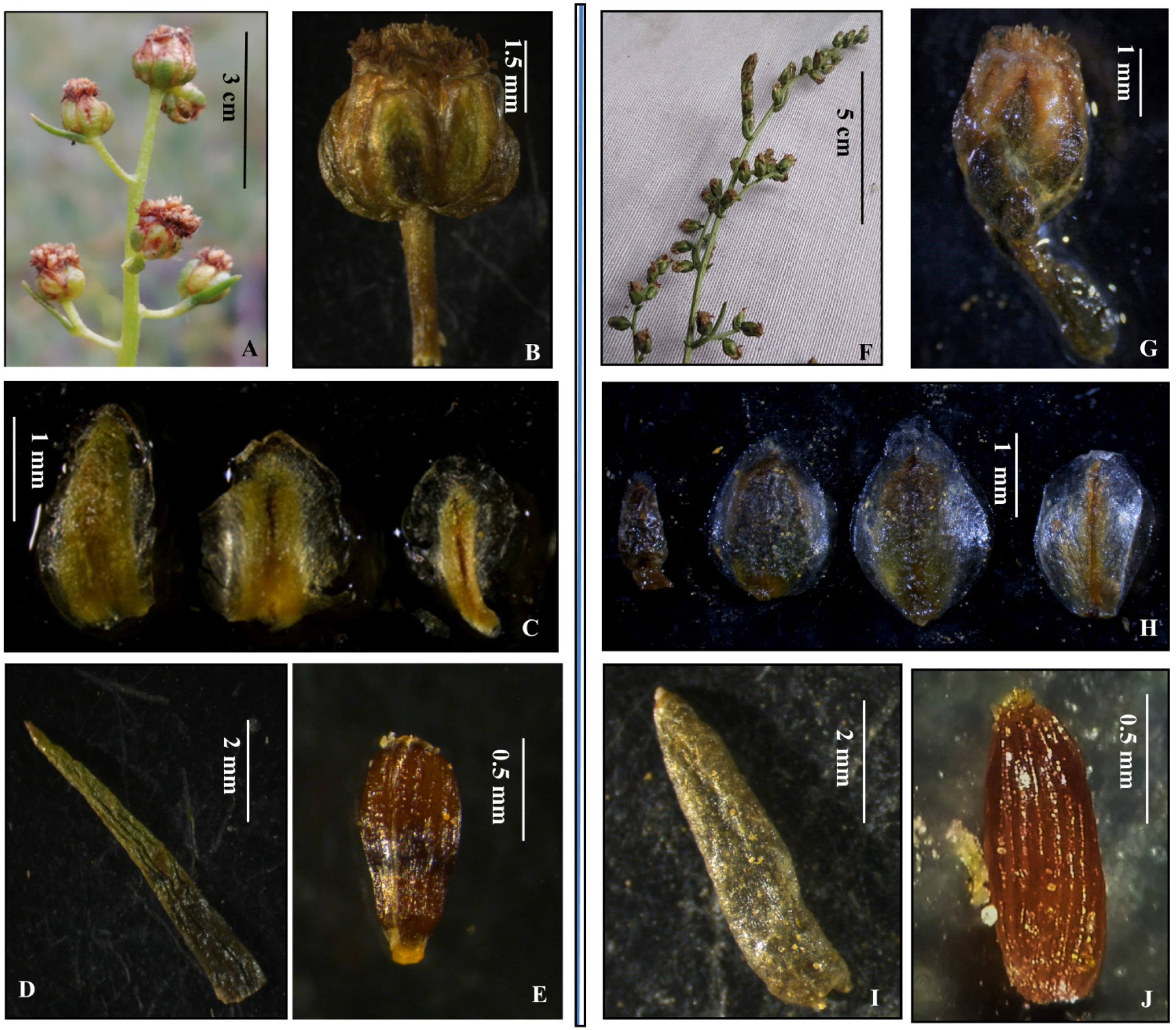

Comparison of distinguishing characters between Artemisia kargilensis (A–E) and A. salsoloides (F–J). A, F. Inflorescence. B, G. Capitula. C, H. Phyllaries. D, I. Bracteole. E, J. achene.

Comparison of distinguishing characters between Artemisia kargilensis with A. salsoloides and A. saposhnikovii.
Perennial subshrub, 40–70 cm tall. Root rhizomatous, rootstock branched. Stems 8–20, upright, semi-solid, light green to purplish-green, grooved, glaucous or densely tomentose. Leaves sessile, stipulate, dark green, rachis winged, glabrous or densely tomentose; segments linear-lanceolate to narrowly oblong, entire, obtuse to acute; basal and lower cauline leaves ovate: tri-lobed, 2–5 × 2–3 cm; middle cauline leaves broadly ovate, 2-pinnatisect, 3–6 × 2.5– 3.5 cm; upper cauline leaves and leaf-like bracts linear, trilobed, entire, 1–3 cm long. Synflorescence erect, panicle lax, lateral inflorescence branches 4–8 cm long. Capitula heterogamous, globose, 2–3 × 1–2 mm, pedicel 2–5 mm long, bracteole linear, 2–6 mm long. Involucre 3-seriate, phyllaries glabrous, ovate to obovate: outermost phyllary ovate, 1.5–3 × 0.5–1 mm, apices obtuse, narrowly hyaline margin; middle phyllary broadly ovate, 1–2 × 0.5–1.6 mm, glabrous, wide hyaline margin, apices obtuse to rounded; innermost phyllary broadly obovate, glabrous, hyaline margin at the upper parts. Receptacle hemispherical, glabrous, 0.2–0.4 mm diameter. Florets yellow: marginal female florets 8–18, pistillate, fertile, corolla 2-dentate, 0.7–1 mm long, narrowly tubular, stigma branches exserted, length of stigma branches 0.5–1 mm, length of style 0.8–1 mm; disc florets 16–28, functionally staminate, corolla 1–2 mm long, 5-dentate, cuneate-shaped, stigma bi-fid, branches 0.3–0.6 mm, style 0.8–1.5 mm, ovary abortive, length of anther lobes 0.7–1 mm, filaments 0.7–1 mm. Achenes dark brown, obovoid, glabrous, striated, with terminal corolliform scar, 0.8–1 × 0.4–0.6 mm long.
Phenology: Flowering from June–July; fruiting from July– September.
Etymology: The specific epithet is derived from the study area, i.e., Kargil, where from the taxon is described for the first time.
Distribution: The species grows abundantly across the area of Kargil, Ladakh: Suru valley, Baroo, Drass, Sapi, and Zanskar. It grows at an altitudinal range of 2,300–3,200 m a.s.l.
Habitat: Roadside, along the banks of Suru River, cultivated field areas and rocky slopes.
Conservation status: Artemisia kargilensis is widely spread across an area of 10,000 km2 in the Kargil district of Ladakh. Since the newly described species has a wide distribution range, it is unlikely to be affected by threats driven by natural and anthropogenic activities in the near future. Thus, it has the potential to play a key role in maintaining the basic ecosystem functions and providing essentials for the survival of animal life. Future biodiversity surveys in the unassessed areas across Ladakh are expected to report more populations of this new species.
Note: The discovery of new species is the primary tool to achieve the global biodiversity inventory (Thiele et al., 2021). In particular, the global biodiversity hotspots in the developing world which harbor the highest proportion of biodiversity deserve research priority in the field of taxonomy (Dar and Khuroo, 2020). Taxonomic studies on the genus Artemisia in the Indian subcontinent remain insufficient, with most areas of the Himalayan biodiversity hotspot region still under investigation. Few previous studies on this genus in India were mostly based on cyto-taxonomic characters (Khoshoo and Sobti, 1958; Bhat et al., 1974; Kaul and Bakshi, 1984). The present study conducted in the Trans-Himalayan region of Ladakh aimed to present a new species with diagnostic characteristics such as the glabrous receptacle, heterogamous capitula with outer florets female and central florets morphologically hermaphrodite but functionally male, establishes the taxonomic position of this new species within Artemisia subg. Dracunculus. In gross morphology, the new species resembles A. salsoloides and A. saposhnikovii, but it differs in habit 40–70 cm tall, leaf rachis winged, marginal female florets 8–18, disc florets 16–28, capitula globose, pedicel 2–5 mm long, bracteole linear, 2–6 mm long, margins flat, involucre 3-seriate, innermost phyllary broadly obovate, 1–1.8 × 1–1.2 mm and achenes obovoid. In addition, A. kargilensis vary in habitat altitudinal range also (i.e., 2,300– 3,200 m a.s.l.). A detailed comparison of the delimiting taxonomic characters between A. kargilensis and A. salsoloides is provided (Fig. 4, Table 1).
Reporting new species contributes significantly to enriching biodiversity and plays a vital role in ecosystem health and stability. It does so by filling unoccupied ecological niches, introducing genetic diversity ultimately leading to adaptation, and also by providing various ecosystem services such as pollination, decomposition, and nutrient cycling (Kawecki, 2008). This enhancement of ecosystem services benefits both natural environments and human societies. Furthermore, the exploration of chemical properties and genetic traits of Artemisia species from the Himalayas in the future could potentially lead to valuable medical applications, building upon compounds like artemisinin that are already used in various treatments like Artemisia annua L. in treatment of malaria (Ferreira and Janick, 1996). Therefore, comprehensive documentation of the genus Artemisia is crucial for understanding the intricate relationships within ecosystems, aiding conservation efforts, and ensuring the sustainable management of the earth’s biodiversity, especially in ecologically sensitive regions like the Himalayas. The wide distribution range of this new species across the study area indicates its ability to thrive in different environments highlighting the species’ capacity to adjust to varying conditions, and showcasing the flexibility of adaptive evolution (Hulme, 2005; Kawecki, 2008). Such adaptability is crucial for the survival of the species and demonstrates its resilience in the face of changing landscapes and environmental challenges.
An identification key of new species and its closely related taxa
1. Habit 40–70 cm; leaf rachis winged; capitula globose, bracteole apices acuminate, margins recurved ············· ··································································· A. kargilensis
1. Habit 20–40 cm; leaf rachis wingless; capitula oblong, ovoid to ovoid-sub-globose, bracteole apices acute, margins flat.
2. Outer phyllary 2-seriate, number of marginal female florets 5–6, number of disc florets 10–14; achene oblong ················································· A. salsoloides
2. Outer phyllary 1-seriate, number of marginal female florets 4–5, number of disc florets 4–6; achene oblong or oblong-obovoid ············ A. saposhnikovii
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Honorary Director, Centre for Biodiversity & Taxonomy, Department of Botany, University of Kashmir, for providing necessary facilities to carry out the work. We also thank Dr. K. N. Gandhi, Senior Nomenclature Registrar, Harvard University, for his valuable comment on the name of the new species. We thank the staff and research students at BIOTA lab, Centre for Biodiversity & Taxonomy, University of Kashmir for kind help. The first author acknowledges Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi, for support during the present work under the fellowship number: 09/251(0145)/2019-EMR-I. The financial support received from SERB-DST, Government of India, New Delhi under CRG/2022/006606 to Anzar A. Khuroo is greatly acknowledged. We are grateful to the Editor and reviewers for their critical comments which have improved the quality of the manuscript.
Notes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.