INTRODUCTION
Carex L. (Cyperaceae), with about 2,000 species is one of the largest monocot genera (Dai et al., 2010; Global Carex Group, 2021; WCSP, 2022). It is found worldwide in various habitats except Antarctica (Kükenthal, 1909; Ohwi, 1936; Egorova, 1999; Ball and Reznicek, 2003; Dai et al., 2010; Global Carex Group, 2016; Hoshino et al., 2020). A recent revision of the genus from Korea revealed 157 species in 40 sections (Oh, 2006, 2007, 2018). Over the past ten years, new or unrecorded sedges have occasionally been reported from Korea: Carex aequialta Kük. (Ji et al., 2014a), C. chungii Z. P. Wang (Nam et al., 2014), C. multifolia Ohwi (Nam et al., 2014), C. rugata Ohwi (Ji et al., 2014b), C. scoparia Schkuhr ex Willd. (Cheon et al., 2014), C. taihokuensis Hayata (Masaki et al., 2014), C. tsushimensis (Ohwi) Ohwi (Nam et al., 2014), C. tokuii J. Oda & Nagam. (Oda et al., 2017), C. brevispicula G. H. Nam & G. Y. Chung (Nam et al., 2020), and C. molestiformis Reznicek & Rothrock (Ko et al., 2020).
During a plant diversity field survey in Korean Peninsula, an unrecorded sedge, Carex foraminata C. B. Clarke was found in slope of evergreen broad-leaved forests from Jeollanam-do, Korea. Carex foraminata belongs to section Mitratae Kük. The sect. Mitratae ca. 45−60 species that are mainly distributed in central, eastern, and southeastern Asia, with a few species extending to Australia, New Zealand, and Europe (Dai et al., 2010; Hoshino et al., 2020). With sect. Mitratae is easily distinguished from other sections by its achenes, trigonous in cross-section, ovoid, rhombic-ovoid or obovoid in outline, and usually with an annulate-discoid appendix at apex (Kükenthal, 1909; Dai et al., 2010; Chung and Im, 2020; Nam et al., 2020; Yang and Liu, 2020). In Korea, 25 species of the sect. Mitratae, including one endemic, C. sabynensis Less. ex Kunth var. leiosperma Ohwi (Nam, 2017; Oh, 2006, 2007, 2018). They grow sunny, wet places in forests and roadsides and bloom in early spring (Hoshino et al., 2011; Chung and Im, 2020).
We here formally report the first occurrence of the C. foraminata in Korea (Figs. 1, 2). The distribution of C. foraminata in Korea have been newly media reported by National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) in 2020 and assigned Korean name as Cheno-gong-sa-cho (천공사초), but the formal report with accurate nomenclature and full description of the species with detailed information of distribution has not been made. Here, we provide a description, illustrations, a taxonomic key to related taxa as well as habitat details.
TAXONOMIC TREATMENT
Carex foraminata C. B. Clarke, J. Linn. Soc. Bot. 36: 285, 1903.—TYPE: CHINA. Zhejiang, Mts. Ningbo, 1889, E. Faber 63 (syntype: K, K000960856, photo!); Zhejiang and Jiujiang, without date, C. Maries s.n. (syntype: K, K000960857, photo!); Jiangxi, Mts. Jiujiang, without date, E. Faber 1139 (syntype: K, K000960858, photo!).
Korean name: Gu-meong-sa-cho (구멍사초).
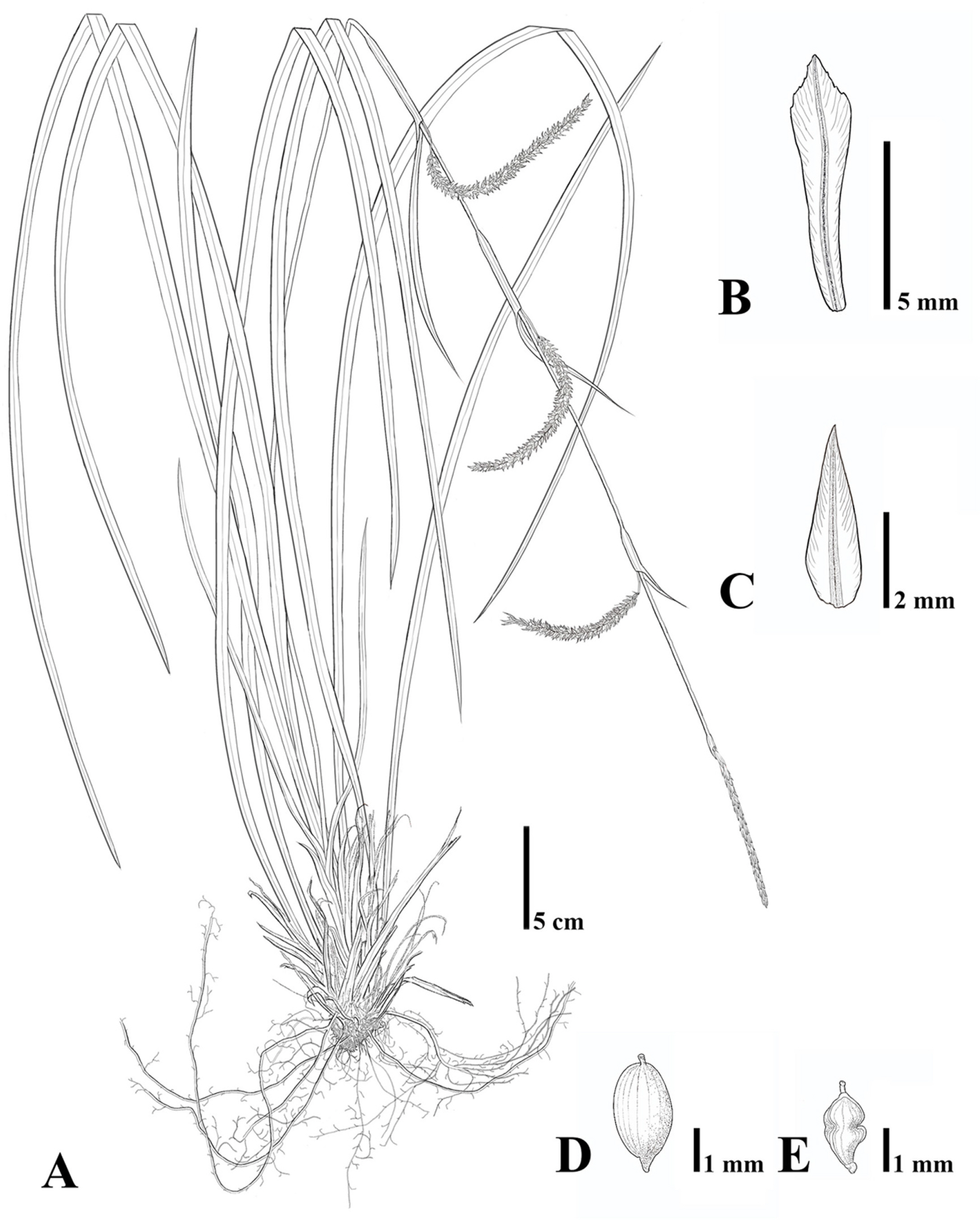
Plants perennial, densely cespitose. Rhizome short, covered with fibrous remains of old leaf sheath, fibrous roots. Culms central and lateral, trigonous, 40−70 cm tall, 2−3 mm thick. Leaves basal; blades dark green, linear, shorter than culms, 40−80 cm long, 5−7.5 mm wide, apex acuminate, margins scabrid, flat, leathery, upper surface densely granular; basal sheaths 3−6 cm long, with purple vertical stripes, basal part reddish brown. Bracts 4−5, sheaths 2−5 cm; lower bracts shortly leaflike, slightly longer than or equaling spike; middle and upper ones bristlelike or setaceous, shorter than spikes. Spikes 4−6, remotely; terminal spike staminate or rarely with a few pistillate flowers, linear-cylindric, 4.5−7.5 cm × 3−5 mm, peduncle 5−8 cm long, densely flowered; lateral spikes pistillate or androgynous with male part up to 1/2 length of spike, linear-cylindric, 5−10 cm × 2−4 mm, densely flowered, usually arcuate, peduncle 2−4.5 cm, slightly exserted but upper ones enclosed in involucral bract sheath. Staminate scales yellowish brown or brown, membranous, obovate-oblong, 6−7 × 1.5−2 mm, apex acute, attenuate or cuspidate. Pistillate scales pale brown-brown on both upper sides, membranous, ovate or oblong-ovate to oblong, 3−4 × 1.5−2 mm, costa pale green, apex acute or acuminate. Stemens 3; filaments filiform, ca. 8 mm, glabrous; anthers linear, ca. 5 mm. Style 0.6−10 mm long, base slightly thickened. Stigmas 3, 1.2−1.5(−3) mm long. Perigynia shorter than pistillate scales, obovate to obovate-elliptic, elliptic, 2−2.3 mm long, many veined, puberulent, base stipitate, apex shortly beaked, emarginated at orifice. Achenes tightly enveloped, yellowish brown or brown, slightly shiny, oblong or elliptic, 1.5−2 mm long, with angles contracted at middle, base with short and bent stipe, apex abruptly contracted into a short cylindric beak.
Flowering: April to May.
Fruiting: May to June.
Distribution and habitat: Carex foraminata has been recognized to be native only to southeastern and southcentral China (Dai et al., 2010). In this study, we report its distribution in Korea. It was found in a southwest island (Hongdo Island) in Korean Peninsula in 2020 and confirmed again at the fruiting season in 2022. This species is distributed in a slope of evergreen broad-leaved forests, at an elevation of 200−300 m a.s.l. Three populations containing ca. 300 individuals are confirmed at the southeastern slope of the hill. The canopy vegetation includes Machilus thunbergii Siebold & Zucc., Neolitsea aciculata (Blume) Koidz., Neolitsea sericea (Blume) Koidz., Castanopsis sieboldii (Makino) Hatus., Quercus acuta Thunb., Camellia japonica L., Eurya japonica Thunb., Aucuba japonica Thunb., Euonymus japonicus Thunb., and Dendropanax trifidus (Thunb.) Makino ex H. Hara; the herbaceous vegetation is made up of Arachniodes aristata (G. Forst.) Tindale, Cyrtomium falcatum (L. f.) C. Presl var. devexiscapulae (Koidz.) Tagawa, Dryopteris erythrosora (D. C. Eaton) Kuntze, Lemmaphyllum microphyllum C. Presl, Clematis terniflora DC., Stauntonia hexaphylla Decne., Ficus erecta Thunb., Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb., Ardisia japonica (Thunb.) Blume, Trachelospermum asiaticum (Siebold & Zucc.) Nakai, Damnacanthus indicus C. F. Gaertn., Dioscorea quinqueloba Thunb., Calanthe insularis S. H. Oh, H. J. Suh & C.-W. Park, Calanthe sieboldii Decne. ex Regel, and Goodyera biflora (Lindl.) Hook. f.
Specimens examined: KOREA. Jeollanam-do: Shinan-gun, Heuksan-myeon, Hongdo-ri, Hongdo Island, 15 May 2020, Jin-Seok Kim kjs20026, kjs20027, kjs20028, kjs20029, kjs20030, kjs20031 (2 sheets), kjs20032 (KB); same locality, cultivated at NIBR, 10 Mar 2021, Jin-Seok Kim kjs21001, kjs21002 (KB); same locality, 10 May 2022, Jung-Hyun Kim KIMJH22001, KIMJH22002, KIMJH22003, KIMJH22004, KIMJH22005, KIMJH22006, KIMJH22007 (KB).